
Performance Characteristics Of Materials
q
The Property that lets electrical current flow through a material

The Property that lets thermal energy flow through a material

A material's ability to break down over time as a result of biological activity (being broken down by microorganisms)

A material's ability to withstand chemical attack without being broken down
A material's ability to withstand rusting from water without being broken down
The ability allowing a material to resist forces from all directions (compressive, tensile, bending, shear, torsional).
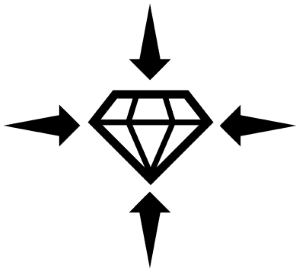
The ability allowing an object or material to reassume its normal shape after being stretched or compressed.

A material's ability to be permanently deformed and retain its deformed shape
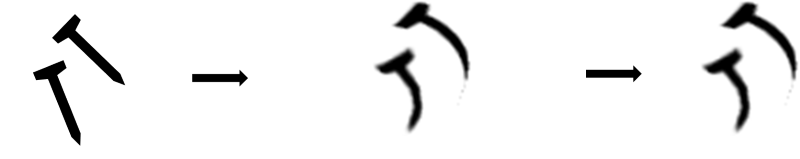
A materia's ability to be deformed by compression without being torn / cracked.

The ability of a material to be drawn/stretched out thin (usually into wires)

A material's ability to withstand indentation / abrasion / scratching.
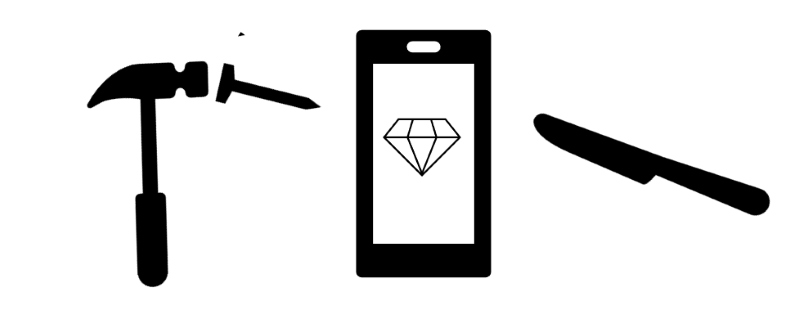
A material's ability to absorb impact force without fracture.
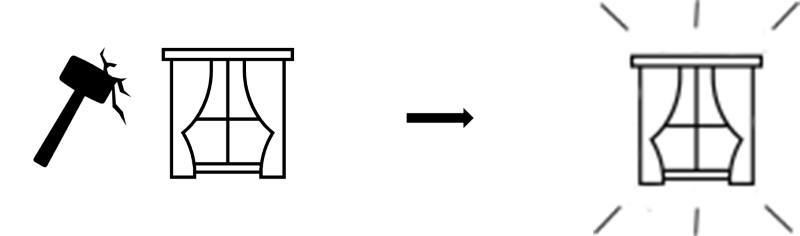
A material's ability to withstand wear, pressure, and damage.
The following page of notes will cover:
- Physical characteristics (Physical properties)
- Mechanical characteristics (Mechanical properties / Working properties)
Physical characteristics
Electrical conductivity:
The Property that lets electrical current flow through a material

Thermal conductivity:
The Property that lets thermal energy flow through a material

Biodegradability:
A material's ability to break down over time as a result of biological activity (being broken down by microorganisms)

Chemical resistance:
A material's ability to withstand chemical attack without being broken down
Corrosion resistance:
A material's ability to withstand rusting from water without being broken down
Mechanical (Working) characteristics
Strength (Tensile, Compressive, Torsional, Shear, Bending):
The ability allowing a material to resist forces from all directions (compressive, tensile, bending, shear, torsional).

Elasticity:
The ability allowing an object or material to reassume its normal shape after being stretched or compressed.

Placticity:
A material's ability to be permanently deformed and retain its deformed shape
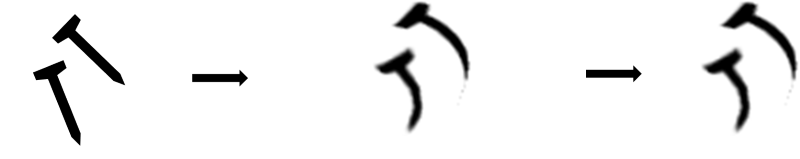
Malleability:
A materia's ability to be deformed by compression without being torn / cracked.

Ductility:
The ability of a material to be drawn/stretched out thin (usually into wires)

Hardness:
A material's ability to withstand indentation / abrasion / scratching.

Toughness:
A material's ability to absorb impact force without fracture.

Durability:
A material's ability to withstand wear, pressure, and damage.
